High-End Gift Boxes Returned Due to Color Deviation: How to Address the Pain Points in the Packaging Industry (Part 1)
 Sep 30,2025
Sep 30,2025In today’s fiercely competitive business landscape, packaging serves as the "first impression" of a product, and its importance is self-evident. For high-end gift boxes, they bear an even greater responsibility of embodying brand image and conveying emotions—every detail can make or break the outcome. However, incidents of high-end gift boxes being returned due to color deviation occur from time to time. This not only brings economic losses to manufacturers and damages brand reputation but also exposes deep-seated pain points in color management within the packaging industry. This article will delve into the reasons behind this phenomenon and explore feasible solutions for the packaging industry to resolve color deviation and other related pain points.
Color Deviation-Related Returns of High-End Gift Boxes: Phenomenon and Impacts

High-end gift boxes usually attract consumers with their exquisite design, high-quality materials, and sophisticated craftsmanship. As a key visual element, color needs to accurately restore the original design intent. In reality, however, due to various factors, the final color of gift boxes often deviates from the design draft or customer expectations.
A company specializing in high-end jewelry gift packaging customized a batch of limited-edition gift boxes for a well-known jewelry brand. The main color of the gift boxes in the design draft was a deep, elegant sapphire blue—intended to complement the dazzling luster of the jewelry and highlight the product’s high-end quality. Yet when the jewelry brand received the finished products, it found that the color of the gift boxes tilted towards blue-green, showing a clear deviation from the sapphire blue in the design draft. This mistake rendered the batch of gift boxes unusable for on-time delivery; the jewelry brand had to urgently adjust its promotion plan and request the packaging company to remake the boxes. For the packaging company, this meant a significant increase in costs—including raw materials, labor, and time—due to re-production. It also faced the risk of compensation for breach of contract due to delayed delivery. More seriously, this color deviation incident severely damaged the packaging company’s credibility in the eyes of the customer: the jewelry brand questioned its professional capabilities, casting a shadow over the prospects of future cooperation.
From a macro perspective, such color deviation-related return incidents are not isolated cases. In the high-end gift box market, customers have extremely high requirements for packaging quality—even minor color deviations may trigger returns. According to incomplete statistics, in the field of high-end gift packaging, the return rate caused by color deviation accounts for approximately 5% to 10% of total orders. Though this ratio may seem low, given the high added value and customized nature of high-end gift boxes, the economic losses and brand impact it causes should not be underestimated. Frequent color deviation-related returns also reflect systemic issues in color control within the packaging industry, which urgently need to be resolved.
Root Causes of Color Deviation: Intertwined Factors
1. Differences in Raw Materials
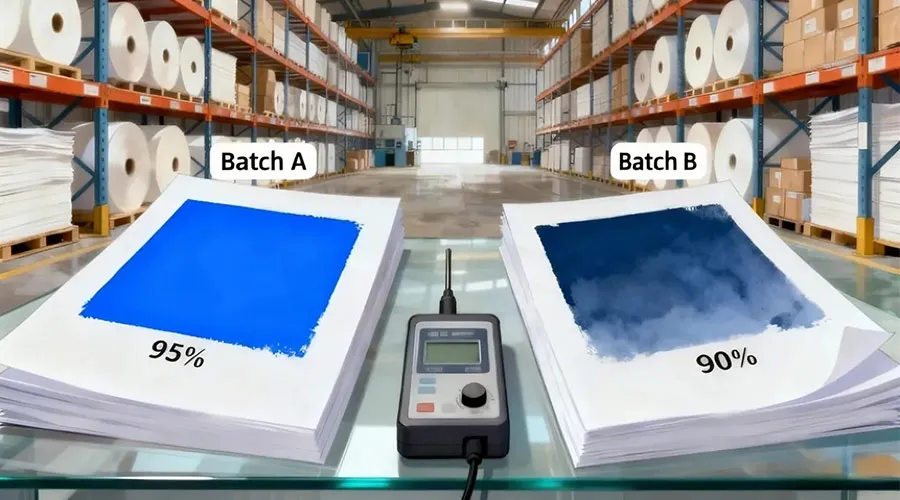
•Impact of paper properties: As one of the main raw materials for high-end gift boxes, paper properties play a crucial role in color presentation. First is paper whiteness—paper from different batches or manufacturers may vary in whiteness. For example, for a certain brand of white cardboard, the whiteness of Batch A may be 95%, while that of Batch B may only be 90%. When printing the same color pattern on these two batches of paper, the color on Batch A (with higher whiteness) will appear brighter and more vivid, while the color on Batch B will be relatively dull. Even within the same batch, paper whiteness may change during storage due to environmental factors such as light and humidity. Second, paper absorbency varies, affecting the degree and speed of ink absorption. Paper with high absorbency allows ink to penetrate quickly, leading to lighter colors after drying; paper with low absorbency retains more ink on its surface, resulting in relatively darker colors. For instance, uncoated kraft paper has high absorbency, while coated art paper has low absorbency—printing the same ink on the two types of paper produces noticeably different color effects.

•Ink quality and stability: The quality and stability of ink are directly related to the accuracy and consistency of printed colors. Inks of different brands and models differ in pigment composition, particle size, and dispersibility—these differences lead to variations in color performance during printing. Some low-quality inks may experience pigment precipitation or stratification during printing, causing uneven colors or hue deviations. In addition, performance indicators such as ink’s light resistance and weather resistance are also important. For example, some inks tend to fade under prolonged light exposure; if high-end gift boxes are exposed to light during display or storage, their color will gradually change, failing to match the original design effect.
2. Issues with Printing Processes and Equipment
•Differences in printing methods: Currently, common printing methods in the packaging and printing industry include offset printing, gravure printing, flexographic printing, and screen printing. Each method has its unique ink transfer principle and color performance characteristics. Offset printing transfers ink via a blanket, resulting in a relatively thin ink layer—it is suitable for printing fine patterns and continuous-tone images, but its color saturation and vividness may be lower than that of gravure printing. Gravure printing transfers ink directly to the substrate, creating a thick ink layer with bright, high-saturation colors; however, it may be less precise than offset printing when printing fine lines and dots. Flexographic printing and screen printing also have their own features: flexographic printing is suitable for large-area solid printing and some flexible packaging printing, while screen printing is often used for special-effect printing (e.g., matte, gold stamping). Due to the varying color performance of different printing methods, arbitrary changes to the printing method during production or selection of a method incompatible with the gift box design requirements can easily lead to color deviation.
•Precision and aging of printing equipment: The precision of printing equipment is decisive for color restoration. Printing high-end gift boxes usually requires high-precision equipment to ensure color accuracy and consistency. However, with long-term use, key components of the equipment—such as printing cylinders, blankets, and ink fountains—gradually wear out, leading to unstable ink transfer volume and dot distortion, which in turn cause color deviation. For example, worn printing cylinders have reduced surface flatness, resulting in uneven ink distribution during printing and inconsistent color depth on the printed product. In addition, inaccurate equipment calibration is another important cause of color deviation. If the color management system of the printing equipment is not properly calibrated, or if regular calibration according to standards is not performed during production, it will be impossible to accurately convert the colors in the design draft into printed colors.
3. Incomplete Color Management Processes
•Non-standard color mixing: In packaging and printing production, color mixing is a key link in achieving accurate color restoration. However, many enterprises have non-standard operations in the color mixing process. Some color mixers rely excessively on personal experience, lacking scientific color mixing methods and standard procedures. For example, when preparing spot color inks, they determine the proportion of various inks solely through visual observation and experience, rather than using professional color mixing instruments for precise measurement and analysis. This approach is highly influenced by the subjective factors of the color mixer—colors mixed by different operators may vary, and even the same operator may struggle to ensure color consistency when mixing at different times or in different environments. Furthermore, insufficient consideration of factors such as ink batch differences and paper properties during color mixing can also lead to inaccurate color preparation and subsequent color deviation.
•Lack of a standardized color management system: A comprehensive standardized color management system should cover the entire production process, from design draft creation and proofing to printing and finished product inspection. However, many packaging enterprises have not yet established such a system. In the design phase, designers may use different color modes and software, resulting in inconsistent color display of the design draft on different devices. In the proofing phase, due to differences in color performance between proofing equipment and printing equipment, failure to calibrate and match through effective color management methods will lead to color deviation between the proof and the final printed product. During the printing process, the lack of standardized control over key factors such as ink, paper, and printing parameters makes it difficult to ensure color stability in production. In the finished product inspection phase, the absence of unified color deviation standards and testing methods makes it impossible to accurately determine whether a product is qualified, easily allowing substandard products to enter the market.
Looking for a reliable packaging box manufacturer? Contact Juxin now!